
The main factor causing lung cancer in non-smokers is Radon.
How Does Radon Affect Your Health?
Radon seeps into the lining of your lungs and emits radiation when you breathe it in. It can harm the cells there over an extended period of time and result in lung cancer.
- In the US, radon is thought to be the cause of 21,000 deaths annually.
- Although everyone is exposed to radon, certain populations identified in the literature are more likely to have elevated radon levels. Furthermore, some communities are more vulnerable to the negative health impacts of radon exposure.
- According to estimates, those who smoke cigarettes have a 10 to 20 times higher risk of developing lung cancer from radon exposure than people who have never smoked.
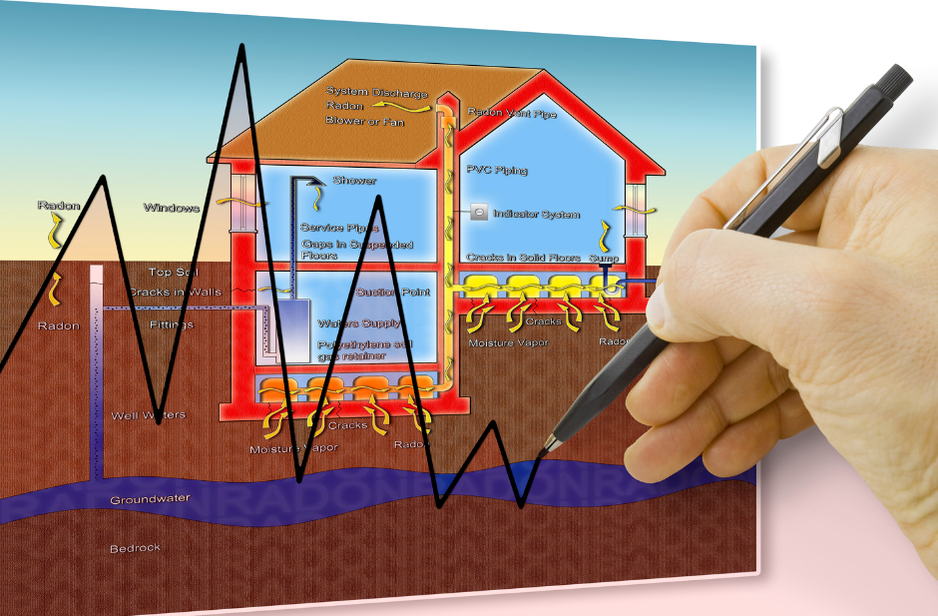
The radioactive particles in radon gas might become stuck in your lungs when you breathe it in. These radioactive particles raise the possibility of lung cancer over time. Years may pass before you notice signs of health issues, years may pass.

According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), radon is responsible for 21,000 lung cancer deaths annually. The main environmental factor causing cancer is radon. After smoking, it is the second most common cause of lung cancer. Compared to persons who do not smoke and are exposed to the same radon levels, smokers have a 10 times higher probability of getting lung cancer from radon exposure.
The risk of developing lung cancer from radon exposure is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- The age at exposure,
- Time spent being exposed
- Radon concentration in relation to time and age
- Using cigarettes
- Time spent and attention focused on various areas of the home, on commute routes, and in the business
- Source of water
- Radon levels are frequently greater in the winter and lower in the summer in colder climates.
- Static-prone seasons—between April and October, for example, there may be an increase in the degree to which radon progeny adhere to dust particles.
- The amount of time since the exposure began.
According to research, drinking water with high radon levels may also be dangerous, though the dangers are far smaller than those involved with breathing radon-containing air.
